Understanding Cyber Security and Its Importance
Cyber security involves protecting systems, networks, and data from cyber threats and attacks. As digital dependence increases, so does the risk of hacking, malware, and data breaches. Effective cyber security measures safeguard sensitive information, maintain trust, and ensure business continuity. It’s essential for individuals and organizations to stay vigilant and proactive in defending against evolving cyber threats. Implementing robust security protocols helps prevent financial loss, legal issues, and reputational damage. Regular updates, strong passwords, and employee training are critical components of a comprehensive cyber security strategy. With cybercriminals becoming more sophisticated, staying informed about latest threats and defense mechanisms is vital for ongoing protection. Cyber security is not just an IT concern but a fundamental aspect of modern digital life that requires constant attention and adaptation.
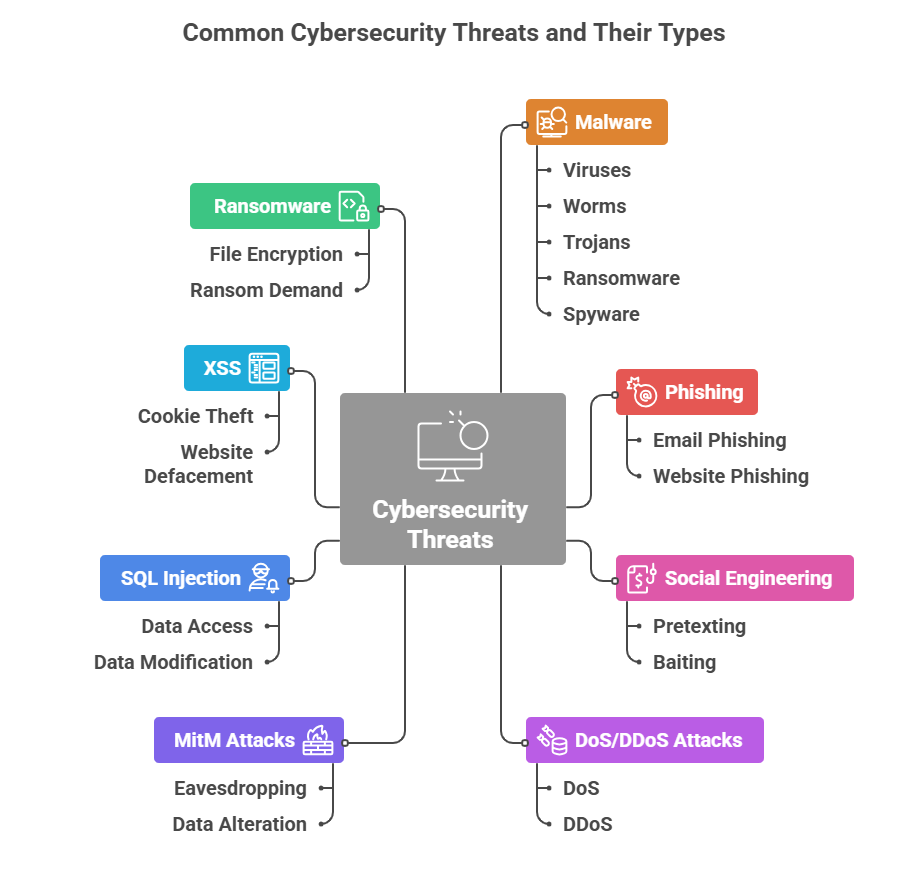
Common Types of Cyber Threats and Attacks
Cyber threats come in various forms, each capable of causing significant harm. Malware, including viruses, ransomware, and spyware, infects devices and networks, often demanding ransom or stealing data. Phishing attacks deceive individuals into revealing confidential information through fake emails or websites. Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks overload servers, rendering websites inaccessible. Man-in-the-middle attacks intercept data during transmission, risking data theft. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are sophisticated, targeted attacks often linked to nation-states. Zero-day exploits take advantage of unknown vulnerabilities before patches are available. Understanding these threats enables organizations and individuals to implement targeted defenses. Regular security assessments, user awareness, and advanced detection tools are essential to mitigate these risks and safeguard digital assets.
Best Practices for Enhancing Cyber Security
Implementing best practices significantly boosts cyber security defenses. Use strong, unique passwords for different accounts, and enable multi-factor authentication to add layers of security. Regularly update software, operating systems, and security patches to fix vulnerabilities. Back up data frequently and store it securely offline or in the cloud. Educate employees about phishing scams, social engineering, and safe browsing habits. Deploy firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection systems to monitor and block malicious activities. Limit access to sensitive information based on roles and responsibilities. Conduct periodic security audits and penetration testing to identify weaknesses. Developing an incident response plan ensures quick action during a breach. Staying vigilant and proactive helps prevent cyber attacks and minimizes potential damage, making cyber security an ongoing process.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Defense
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming cyber security by enhancing threat detection and response. AI systems analyze vast amounts of data to identify unusual patterns indicative of cyber threats. Machine learning algorithms adapt and improve over time, detecting new and evolving malware more efficiently than traditional methods. AI-powered security tools can automatically respond to threats, reducing response times and limiting damage. They also assist in identifying vulnerabilities and prioritizing security measures. However, cybercriminals also use AI to develop more sophisticated attacks, creating a continuous arms race. Organizations integrating AI into their cyber security frameworks gain a critical advantage in early threat detection and automated defense. As AI technology advances, its role in securing digital environments will become increasingly vital and indispensable.
Future Trends and Challenges in Cyber Security
The future of cyber security involves adapting to rapidly changing technology landscapes and emerging threats. Quantum computing poses potential risks by breaking traditional encryption methods, requiring new cryptographic solutions. The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices expands attack surfaces, demanding better security protocols. Cloud security remains a priority as more data moves online, necessitating advanced access controls and encryption. Additionally, increasing reliance on AI introduces new vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit. Privacy concerns and regulatory compliance will shape future security policies. The challenge lies in balancing technological innovation with robust security measures. Continuous education, investment in new security tools, and global cooperation are essential to address these evolving challenges effectively. Staying ahead in cyber security will be critical for safeguarding digital futures.